opencv-python เบื้องต้น บทที่ ๑๔: การยุบย่อหรือคลุมล้อมเค้าโครง
เขียนเมื่อ 2020/06/28 19:12
แก้ไขล่าสุด 2024/02/22 10:23
ต่อจาก บทที่ ๑๓
บทที่แล้วได้แนะนำการสร้างเส้นเค้าโครงในเบื้องต้นไปแล้ว สำหรับบทนี้จะเขียนถึงการนำเค้าโครงที่ได้มาลดรูปลงโดยยุบย่อหรือนำกรอบสี่เหลี่ยมมาคลุม
การประมาณเพื่อยุบย่อเค้าโครง
เค้าโครงที่สร้างขึ้นมาได้จาก cv2.findContours() นั้นจะแสดงตำแหน่งจุดที่จะวางเพื่อใช้เส้นตรงคั่น ถ้าตรงไหนเป็นเส้นโค้งก็จะต้องใช้หลายจุดเพื่อกำหนดจุดของเส้นเค้าโครง
ในบางครั้งเราอาจไม่จำเป็นต้องใช้จุดอย่างละเอียดมากถึงขนาดนั้น แต่ต้องการลดความซับซ้อนลงสักหน่อย ให้จุดของเค้าโครงแค่พอคลุมคร่าวๆ แต่ช่วยให้เรียบง่ายขึ้น ประหยัดที่เก็บข้อมูลขึ้น
ใน opencv มีฟังก์ชัน cv2.approxPolyDP() ซึ่งใช้อัลกอริธึมของดักลาส-พอยเกอร์ (Douglas–Peucker algorithm) เพื่อทำการประมาณเพื่อยุบย่อจุดบนเส้นให้เรียบง่ายขึ้น วิธีการนี้สามารถนำมาใช้กับเส้นเค้าโครงได้
ค่าที่ต้องใส่ในฟังก์ชัน
| ลำดับที่ | ชื่อ | ค่าที่ต้องใส่ | ชนิดข้อมูล |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | curve | ตำแหน่งจุดบนเส้น | np.array |
| 2 | epsilon | ค่าที่กำหนดความละเอียดของการยุบย่อ | float |
| 3 | closed | เป็นเส้นปิดหรือไม่ | True/False |
ตัวแรกคืออาเรย์ที่แสดงตำแหน่งจุดบนเส้น ซึ่งสามารถใช้ผลที่ได้จาก cv2.findContours() แต่ว่าต้องแปลงทีละเค้าโครง
ตัวที่ ๒ คือ epsilon คือค่าความละเอียด ยิ่งใส่ค่ามากก็ยิ่งยุบจนลดรายละเอียดไปมาก
ตัวที่ ๓ นั้นใส่ True หรือ False เพื่อบอกว่าเส้นเค้าโครงเป็นเส้นปิดหรือเปิด ปกติเส้นเค้าโครงในที่นี้เป็นเส้นปิด จึงให้ใส่ True
ตัวอย่าง ลองเอาภาพนี้มาหาเค้าโครง เสร็จแล้วก็ลองวาดเส้นเค้าโครง เทียบดูระหว่างย่อกับไม่ย่อ โดยเทียบระหว่างการย่อด้วยค่า epsilon ต่างกัน
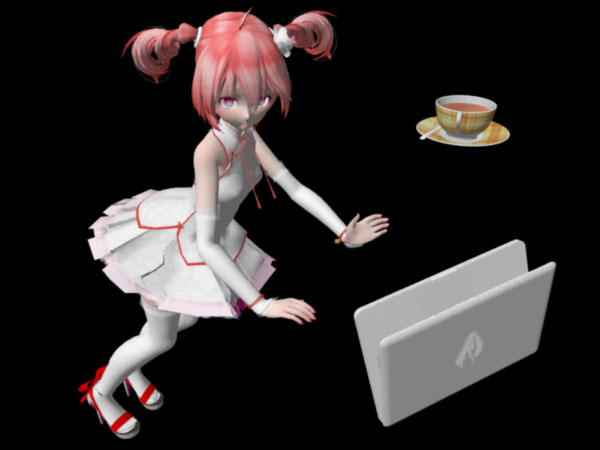

teto14c01.jpg
import cv2
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
teto = cv2.imread('teto14c01.jpg') # อ่านภาพสี
teto_gr = cv2.cvtColor(teto,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) # แปลงเป็นขาวดำ
_,teto_thr = cv2.threshold(teto_gr,10,255,0)
# แปลงสัณฐานเพื่อลดจุดปนเปื้อน
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE,(5,5))
teto_thr = cv2.morphologyEx(teto_thr,cv2.MORPH_CLOSE,kernel)
# หาเค้าโครง
contour,_ = cv2.findContours(teto_thr,cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
n_contour = len(contour)
# สีของเส้นเค้าโครงแต่ละเส้น
si = plt.get_cmap('rainbow')(np.arange(n_contour)/(n_contour-1))[:,[2,1,0]]*255
# สร้างเค้าโครงใหม่ที่ย่อลงจากเดิมเล็กน้อย
contour_dp1 = [cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt,4.5,True) for cnt in contour]
# สร้างเค้าโครงใหม่ที่ย่อลงจากเดิมไปค่อนข้างมาก
contour_dp2 = [cv2.approxPolyDP(cnt,11,True) for cnt in contour]
teto_cnt = teto.copy()
teto_cnt_dp1 = teto.copy()
teto_cnt_dp2 = teto.copy()
for i in range(n_contour):
teto_cnt = cv2.drawContours(teto_cnt,contour,i,si[i],2)
teto_cnt_dp1 = cv2.drawContours(teto_cnt_dp1,contour_dp1,i,si[i],2)
teto_cnt_dp2 = cv2.drawContours(teto_cnt_dp2,contour_dp2,i,si[i],2)
cv2.imwrite('teto14c02.jpg',teto_cnt)
cv2.imwrite('teto14c03.jpg',teto_cnt_dp1)
cv2.imwrite('teto14c04.jpg',teto_cnt_dp2)เค้าโครงที่ยังไม่ได้ยุบ
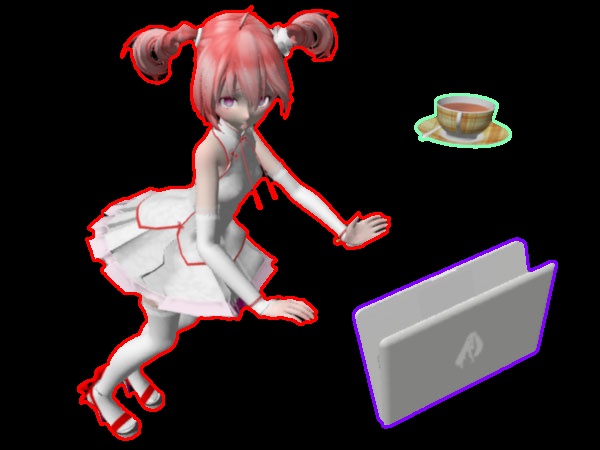

teto14c02.jpg
เค้าโครงที่ยุบไปเล็กน้อย
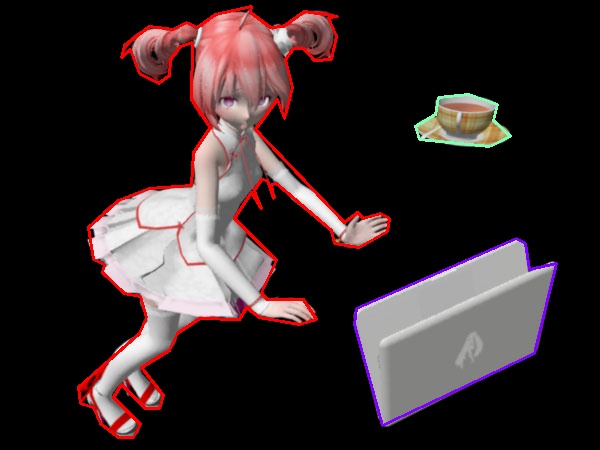

teto14c03.jpg
เค้าโครงที่ยุบไปมาก
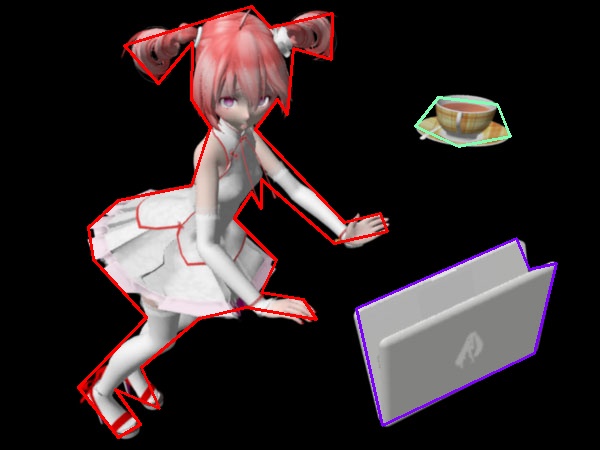

teto14c04.jpg
จะเห็นว่ายิ่งค่า epsilon สูงก็ยิ่งย่อจนเหลือจุดน้อยลงและดูหลวมลงไปมากจนยิ่งไม่ค่อยพอดีกับวัตถุที่ถูกล้อมอยู่
การขึงเส้นเค้าโครง
อีกวิธีที่อาจใช้ในการลดจุดของเส้นเค้าโครงก็คือ จับส่วนที่เว้าแหว่งมาขึงให้เรียบให้หมด
ดูเผินๆอาจคล้ายกับ cv2.approxPolyDP() แต่ว่าวิธีการง่ายกว่า คือดูว่าตรงไหนเว้าลงไปก็ขึงตรงนั้นซะ และข้อดีคือกรอบเค้าโครงที่ย่อแล้วจะยังคงคลุมวัตถุอยู่
ฟังก์ชันสำหรับทำการขึงเส้นเค้าโครงคือ cv2.convexHull()
ค่าที่ต้องใส่มีแค่อาเรย์ของตำแหน่งจุดเค้าโครงเดิม และก็จะได้เค้าโครงใหม่ที่โดนขึงย่อ
เพื่อให้เห็นภาพชัด สร้างอาเรย์เค้าโครงที่มี ๔ จุด แล้วลองใช้ cv2.convexHull() ขึงดู คราวนี้ใช้ matplotlib วาด
cnt = np.array([[[0,0.5]],
[[1,1]],
[[0.5,0.5]],
[[0.8,0]]],dtype=np.float32)
ax = plt.subplot(121,aspect=1)
ax.add_patch(plt.Polygon(cnt[:,0],fc='w',ec='g'))
cnt_ch = cv2.convexHull(cnt)
ax = plt.subplot(122,aspect=1)
ax.add_patch(plt.Polygon(cnt_ch[:,0],fc='w',ec='g'))
plt.show()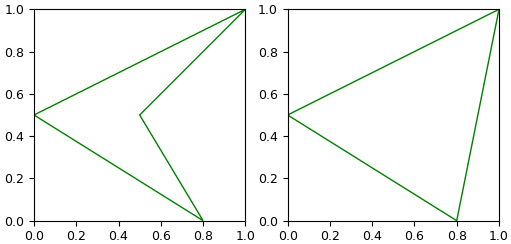
คราวนี้ลองเอาภาพเดิมต่อจากตัวอย่างก่อนหน้านี้มาใช้ cv2.convexHull()
teto_cnt = teto.copy()
for i in range(n_contour):
cnt = cv2.convexHull(contour[i])
teto_cnt = cv2.drawContours(teto_cnt,[cnt],0,si[i],2)
cv2.imwrite('teto14c05.jpg',teto_cnt)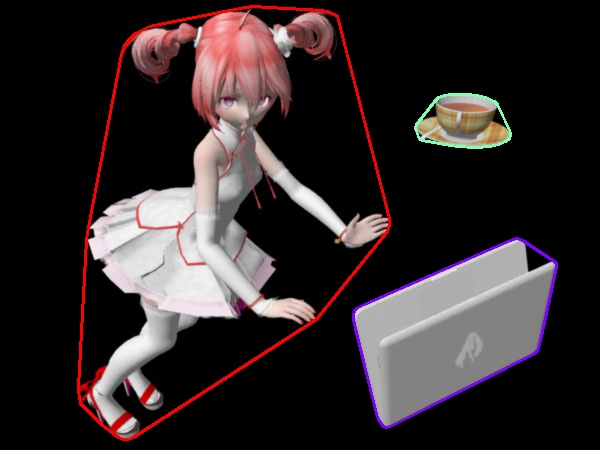
teto14c05.jpg
การตรวจดูว่าจุดบนเค้าโครงถูกขึงตึงหมดหรือยัง
หากมีเส้นเค้าโครงแล้วต้องการดูว่าถูกขึงตึงหมดหรือยังอาจใช้ฟังก์ชัน cv2.isContourConvex() จะคืนค่าเป็น True ถ้าขึงตึงแล้ว และ False ถ้ายังไม่ขึงตึง
ตัวอย่าง ลองสร้างอาเรย์ของจุดเส้นเค้าโครงแบบง่ายๆขึ้นมา วาดดูแล้วดูว่าแบบไหนขึงตึงแล้วหรือไม่
cnt1 = np.array([[[0,0]],
[[1,2]],
[[0,3]],
[[-1,2]]])
cnt2 = np.array([[[0,0]],
[[1,2]],
[[0,1]],
[[-1,3]]])
cnt2_ch = cv2.convexHull(cnt2)
ax = plt.subplot(131,aspect=1,xlim=[-2,2],ylim=[0,4])
ax.add_patch(plt.Polygon(cnt1[:,0],fc='w',ec='m'))
ax = plt.subplot(132,aspect=1,xlim=[-2,2],ylim=[0,4])
ax.add_patch(plt.Polygon(cnt2[:,0],fc='w',ec='m'))
ax = plt.subplot(133,aspect=1,xlim=[-2,2],ylim=[0,4])
ax.add_patch(plt.Polygon(cnt2_ch[:,0],fc='w',ec='m'))
plt.show()
print(cv2.isContourConvex(cnt1)) # ได้ True
print(cv2.isContourConvex(cnt2)) # ได้ False
print(cv2.isContourConvex(cnt2_ch)) # ได้ True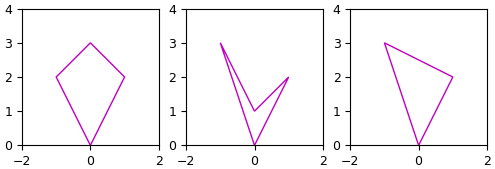
ในที่นี้ cnt1 ขึงตึงอยู่แล้ว cn2 ไม่ได้ขึงตึง แต่เอามาขึงด้วย cv2.convexHull() ก็จะได้เส้นที่ขึงตึง
การสร้างกรอบสี่เหลี่ยมผืนผ้าล้อมเค้าโครง
เค้าโครงที่มีโครงสร้างอย่างง่ายที่อาจสามารถสร้างได้ก็คือเป็นเส้นกรอบสี่เหลี่ยมล้อม
ถ้ามีเส้นเค้าโครงอยู่ แล้วอยากหากรอบสี่เหลี่ยมผืนผ้าขนาดเล็กที่สุดที่จะคลุมเส้นเค้าโครงนั้นได้อาจใช้ฟังก์ชัน cv2.minAreaRect()
ฟังก์ชันนี้จะให้ข้อมูลของสี่เหลี่ยมผืนผ้าออกมา โดยให้เป็นทูเพิลตัวเลข ๕ ตัวที่บอกถึง ((x,y),(กว้าง,สูง),มุมเอียง) ออกมา
จากนั้นถ้าใช้ฟังก์ชัน cv2.boxPoints() ก็จะแปลงเป็นตำแหน่งจุดพิกัดมุมของเค้าโครงรูปกรอบสี่เหลี่ยมผืนผ้า เอาค่าที่ได้มาใช้วาดได้
ตัวอย่าง เอาภาพนี้มาหาเค้าโครง แล้วก็หาสี่เหลี่ยมที่ล้อมเค้าโครงนี้
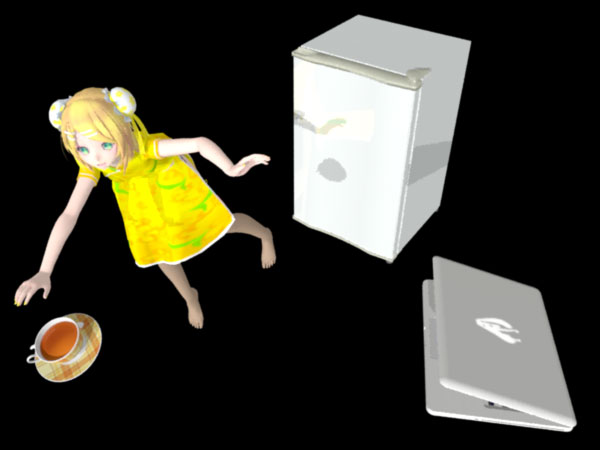

rin14c01.jpg
rin = cv2.imread('rin14c01.jpg')
rin_gr = cv2.cvtColor(rin,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
_,rin_thr = cv2.threshold(rin_gr,10,255,0)
# แปลงสัณฐานเพื่อลดจุดปนเปื้อน
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE,(5,5))
rin_thr = cv2.morphologyEx(rin_thr,cv2.MORPH_CLOSE,kernel)
# หาเค้าโครง
contour,_ = cv2.findContours(rin_thr,cv2.RETR_LIST,cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
n_contour = len(contour)
# สีของเส้นเค้าโครงแต่ละเส้น
si = plt.get_cmap('rainbow')(np.arange(n_contour)/(n_contour-1))[:,[2,1,0]]*255
rin_cnt = rin.copy()
siliam = []
for i,cnt in enumerate(contour):
# วาดเส้นเค้าโครงเดิม
rin_cnt = cv2.drawContours(rin_cnt,[cnt],0,si[i],2)
rect = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt) # หาสี่เหลี่ยมที่ล้อม
siliam.append(rect) # เก็บข้อมูลกรอบสี่เหลี่ยมไว้
for i in range(n_contour):
# แปลงข้อมูลกรอบสี่เหลี่ยมเป็นเค้าโครง ข้อมูลต้องเปลี่ยนเป็น int จึงจะใช้ใน cv2.drawContours() ได้
box = cv2.boxPoints(siliam[i]).astype(int)
# วาดเส้นเค้าโครงสี่เหลี่ยม
rin_cnt = cv2.drawContours(rin_cnt,[box],0,si[i],2)
cv2.imwrite('rin14c02.jpg',rin_cnt)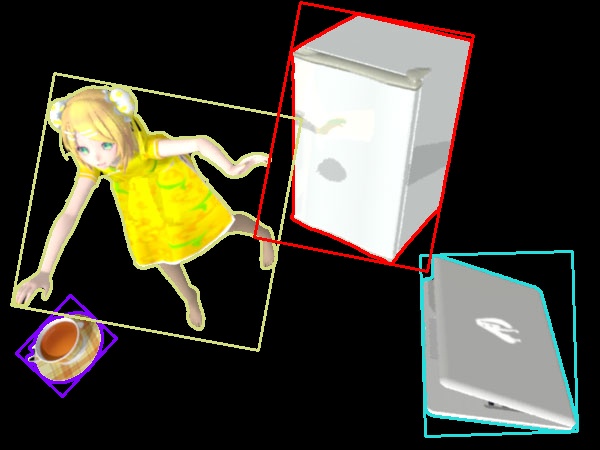
rin14c02.jpg
จะได้เค้าโครงที่เป็นสี่เหลี่ยมผืนผ้าที่บรรจุเค้าโครงเดิมของภาพ
เค้าโครงสี่เหลี่ยมผืนผ้าที่ได้มานี้อาจมีบางส่วนซ้อนกัน หากอยากรู้ว่าพื้นที่ส่วนที่ซ้อนกันอยู่ตรงไหนบ้างอาจใช้ฟังก์ชัน cv2.rotatedRectangleIntersection() โดยใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้จาก cv2.minAreaRect() ใส่ลงไป
ฟังก์ชันนี้จะได้ค่าคืนกลับมา ๒ ตัว ตัวแรกคือเลข 0 หรือ 1 ซึ่งบอกว่าสี่เหลี่ยมทั้งสองมีส่วนที่ซ้อนทับกันหรือไม่ ส่วนอีกตัวคือจุดมุมของบริเวณที่ซ้อนทับกัน
ลองหาส่วนซ้อนทับจากภาพที่แล้วแล้วมาวาดทับลงไปดูได้
# ไล่เทียบดูทีละคู่
for i in range(len(siliam)):
for j in range(i+1,len(siliam)):
mi,tat = cv2.rotatedRectangleIntersection(siliam[i],siliam[j])
# ถ้า mi เป็น 1 แสดงว่ามีส่วนซ้อนทับ ก็เอามาวาด
if(mi):
tat = tat.astype(int) # ต้องเปลี่ยนชนิดข้อมูลเป็น int จึงจะใช้ใน cv2.drawContours() ได้
rin_cnt = cv2.drawContours(rin_cnt,[tat],0,(si[i]+si[j])/2,5)
cv2.imwrite('rin14c03.jpg',rin_cnt)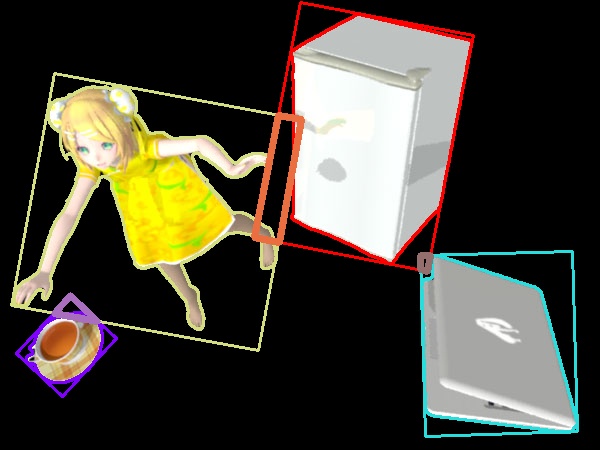
rin14c03.jpg
อ่านบทถัดไป >> บทที่ ๑๕
-----------------------------------------
囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧
หมวดหมู่
-- คอมพิวเตอร์ >> เขียนโปรแกรม >> opencv-- คอมพิวเตอร์ >> เขียนโปรแกรม >> python >> numpy
-- คอมพิวเตอร์ >> เขียนโปรแกรม >> python >> matplotlib