pytorch เบื้องต้น บทที่ ๘: การกำหนดค่าพารามิเตอร์ตั้งต้น
เขียนเมื่อ 2018/09/08 10:14
แก้ไขล่าสุด 2022/07/09 15:44
>> ต่อจาก บทที่ ๗
การกำหนดค่าพารามิเตอร์ตั้งต้นให้เหมาะสมถือเป็นส่วนสำคัญอย่างหนึ่งในการสร้างโครงข่ายประสาทเทียม
ในเนื้อหาโครงข่ายประสาทเทียมเบื้องต้นบทที่ ๑๓ เรื่องการกำหนดค่าพารามิเตอร์ตั้งต้น ได้กล่าวถึงไปแล้วว่าโดยทั่วไปถ้าใช้ฟังก์ชันซิกมอยด์เป็นฟังก์ชันกระตุ้นควรใช้ค่าตั้งต้นแบบซาวีเย (Xavier) แต่ถ้าใช้ ReLU ให้ใช้ค่าตั้งต้นแบบเหอ ไข่หมิง (何恺明, Hé Kǎimíng)
แต่ค่าตั้งต้นของพารามิเตอร์ใน pytorch ได้ถูกกำหนดให้แจกแจงสม่ำเสมอในช่วง -1/√m,1/√m โดยที่ m คือจำนวนตัวแปรขาเข้า
หากต้องการค่าตั้งต้นแบบอื่นก็ต้องกำหนดใหม่เอง
แต่ใน pytorch เองก็ได้เตรียมคำสั่งสำหรับตั้งพารามิเตอร์ตั้งต้นในรูปแบบนั้นให้ อยู่ในมอดูลย่อย torch.nn.init
ค่าตั้งต้นแบ่งเป็น ๒ แบบคืโครงข่ายประสาทเทียมเบื้องต้นบทที่ ๑๓ เรื่องการกำหนดค่าพารามิเตอร์ตั้งต้นอแบบสม่ำเสมอกับแบบปกติ
แบบสม่ำเสมอแบบซาวีเยคือ torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_()
ค่าจะกระจายสม่ำเสมอในช่วง
..(8.1)
โดย m0 คือจำนวนตัวแปรขาเข้า m1 คือจำนวนตัวแปรขาออก
ส่วนแบบเหอ ไข่หมิงคือ torch.nn.init.kaiming_uniform_()
ค่ากระจายในช่วง
..(8.2)
โดยที่ a เป็นค่าที่เราต้องกำหนดใส่ลงไปเอง จะเป็น 0 ถ้าใช้ ReLU แต่ถ้าใช้ LReLU ค่านี้จะใส่ตามความชันฝั่งลบ
ตัวอย่าง
ส่วนกระจายแบบปกติ แบบซาวีเยคือ torch.nn.init.xavier_normal_()
ส่วนเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐานคือ
..(8.3)
แบบเหอ ไข่หมิง torch.nn.init.kaiming_normal_()
..(8.4)
ตัวอย่างการสร้างโครงข่ายประสาทแบบใช้ ReLU หรือ LReLU เป็นฟังก์ชันกระตุ้นระหว่างชั้น (กำหนดโดยค่า a) และให้ใช้ค่าตั้งต้นกระจายแบบปกติแบบเหอ ไข่หมิง
คลาสนี้เวลาใช้ต้องป้อนขนาดขาเข้าและขาออกของแต่ชะชั้นแล้วก็จะสร้างชั้นตามลำดับนั้นให้
เวลาจะทำการฝึกแบบจำลองก็ใช้เมธอด .rianru() ค่าที่ป้อนเข้าใช้เป็นอาเรย์ธรรมดาได้ จะถูกเปลี่ยนเป็นเทนเซอร์เอง
ส่วนเวลานำมาทำนายผลใช้เมธอด .thamnai() ค่าที่ป้อนเข้ามาจะถูกเปลี่ยนเป็นเทนเซอร์เพื่อทำการคำนวณแล้วก็แปลงกลับเป็นอาเรย์
ลองนำมาใช้สร้างโครงข่ายเพื่อจำแนกข้อมูล ๕ กลุ่ม
>> อ่านต่อ บทที่ ๙
การกำหนดค่าพารามิเตอร์ตั้งต้นให้เหมาะสมถือเป็นส่วนสำคัญอย่างหนึ่งในการสร้างโครงข่ายประสาทเทียม
ในเนื้อหาโครงข่ายประสาทเทียมเบื้องต้นบทที่ ๑๓ เรื่องการกำหนดค่าพารามิเตอร์ตั้งต้น ได้กล่าวถึงไปแล้วว่าโดยทั่วไปถ้าใช้ฟังก์ชันซิกมอยด์เป็นฟังก์ชันกระตุ้นควรใช้ค่าตั้งต้นแบบซาวีเย (Xavier) แต่ถ้าใช้ ReLU ให้ใช้ค่าตั้งต้นแบบเหอ ไข่หมิง (何恺明, Hé Kǎimíng)
แต่ค่าตั้งต้นของพารามิเตอร์ใน pytorch ได้ถูกกำหนดให้แจกแจงสม่ำเสมอในช่วง -1/√m,1/√m โดยที่ m คือจำนวนตัวแปรขาเข้า
หากต้องการค่าตั้งต้นแบบอื่นก็ต้องกำหนดใหม่เอง
แต่ใน pytorch เองก็ได้เตรียมคำสั่งสำหรับตั้งพารามิเตอร์ตั้งต้นในรูปแบบนั้นให้ อยู่ในมอดูลย่อย torch.nn.init
ค่าตั้งต้นแบ่งเป็น ๒ แบบคืโครงข่ายประสาทเทียมเบื้องต้นบทที่ ๑๓ เรื่องการกำหนดค่าพารามิเตอร์ตั้งต้นอแบบสม่ำเสมอกับแบบปกติ
แบบสม่ำเสมอแบบซาวีเยคือ torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_()
ค่าจะกระจายสม่ำเสมอในช่วง
..(8.1)
โดย m0 คือจำนวนตัวแปรขาเข้า m1 คือจำนวนตัวแปรขาออก
ส่วนแบบเหอ ไข่หมิงคือ torch.nn.init.kaiming_uniform_()
ค่ากระจายในช่วง
..(8.2)
โดยที่ a เป็นค่าที่เราต้องกำหนดใส่ลงไปเอง จะเป็น 0 ถ้าใช้ ReLU แต่ถ้าใช้ LReLU ค่านี้จะใส่ตามความชันฝั่งลบ
ตัวอย่าง
import torch
lin = torch.nn.Linear(800,1600)
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(lin.weight)
print(lin.weight.min()) # ได้ tensor(-0.0500, grad_fn<=MinBackward1>)
lin = torch.nn.Linear(577,100)
torch.nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(lin.weight,a=0.2)
print(lin.weight.max()) # ได้ tensor(0.1000, grad_fn<=MaxBackward1>)ส่วนกระจายแบบปกติ แบบซาวีเยคือ torch.nn.init.xavier_normal_()
ส่วนเบี่ยงเบนมาตรฐานคือ
..(8.3)
แบบเหอ ไข่หมิง torch.nn.init.kaiming_normal_()
..(8.4)
ตัวอย่างการสร้างโครงข่ายประสาทแบบใช้ ReLU หรือ LReLU เป็นฟังก์ชันกระตุ้นระหว่างชั้น (กำหนดโดยค่า a) และให้ใช้ค่าตั้งต้นกระจายแบบปกติแบบเหอ ไข่หมิง
ha_entropy = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
class Prasat(torch.nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self,m,eta=0.01,a=0):
super(Prasat,self).__init__()
nm = len(m)
for i in range(1,nm):
lin = torch.nn.Linear(m[i-1],m[i])
torch.nn.init.kaiming_normal_(lin.weight,a) # ค่าตั้งต้นน้ำหนัแจกแจงปกติแบบเหอ ไข่หมิง
lin.bias.data.fill_(0) # ไบแอสให้ตั้งต้นเป็น 0
self.add_module('lin%d'%i,lin)
if(i<nm-1): # ใส่ฟังก์ชันกระตุ้นยกเว้นชั้นสุดท้าย
if(a): # ถ้า a>0 ใช้ LReLU
self.add_module('lrelu%d'%i,torch.nn.LeakyReLU(a))
else: # ถ้า a เป็น 0 ใช้ ReLU ธรรมดา
self.add_module('relu%d'%i,torch.nn.ReLU())
self.opt = torch.optim.Adam(self.parameters(),lr=eta)
def rianru(self,X,z,n_thamsam):
X = torch.Tensor(X)
z = torch.LongTensor(z)
for o in range(n_thamsam):
a = self(X)
J = ha_entropy(a,z)
J.backward()
self.opt.step()
self.opt.zero_grad()
def thamnai(self,X):
X = torch.Tensor(X)
return self(X).argmax(1).numpy()คลาสนี้เวลาใช้ต้องป้อนขนาดขาเข้าและขาออกของแต่ชะชั้นแล้วก็จะสร้างชั้นตามลำดับนั้นให้
เวลาจะทำการฝึกแบบจำลองก็ใช้เมธอด .rianru() ค่าที่ป้อนเข้าใช้เป็นอาเรย์ธรรมดาได้ จะถูกเปลี่ยนเป็นเทนเซอร์เอง
ส่วนเวลานำมาทำนายผลใช้เมธอด .thamnai() ค่าที่ป้อนเข้ามาจะถูกเปลี่ยนเป็นเทนเซอร์เพื่อทำการคำนวณแล้วก็แปลงกลับเป็นอาเรย์
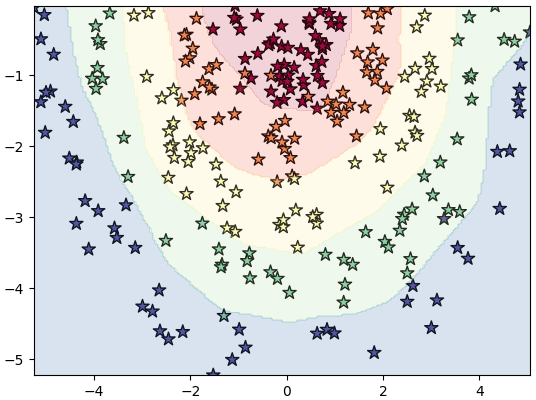
ลองนำมาใช้สร้างโครงข่ายเพื่อจำแนกข้อมูล ๕ กลุ่ม
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
z = np.arange(5).repeat(50)
r = np.random.normal(z+1,0.28)
t = np.random.uniform(-np.pi,0,250)
x = r*np.cos(t)
y = r*np.sin(t)
X = np.array([x,y]).T
prasat = Prasat([2,32,32,32,5],eta=0.1,a=0.2) # โครงข่าย 4 ชั้น โดยใช้ LReLU ที่มีความชันส่วนลบเป็น 0.2
prasat.rianru(X,z,100)
mx,my = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x.min(),x.max(),200),np.linspace(y.min(),y.max(),200))
mX = np.array([mx.ravel(),my.ravel()]).T
mz = prasat.thamnai(mX)
mz = mz.reshape(200,200)
plt.xlim(x.min(),x.max())
plt.ylim(y.min(),y.max())
plt.scatter(x,y,100,c=z,marker='*',edgecolor='k',cmap='Spectral')
plt.contourf(mx,my,mz,alpha=0.2,cmap='Spectral')
plt.show()
>> อ่านต่อ บทที่ ๙
-----------------------------------------
囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧囧
หมวดหมู่
-- คอมพิวเตอร์ >> ปัญญาประดิษฐ์ >> โครงข่ายประสาทเทียม-- คอมพิวเตอร์ >> เขียนโปรแกรม >> python >> pytorch